Hooked: How To Build Habit-Forming Products
by Nir Eyal and Ryan Hoover
Nir Eyal and Ryan Hoover present and discuss about Hook model and how one can build habit-forming products. Human behavior is a very interesting mystery and many factors such as the outside social world influences it to a great extent (read this wonderful book by Jonah Berger, reviewed by me – Behavior – Who Shapes our Choices and Decisions? Power of Social Influence), though we never admit the power of others.
As we all know, the market is filled with many products. The failure rate of new products is very high. So, how to create a space for your product is the first challenge. Then, your product should not be one-stop experiment for consumers. Once a consumer uses your product, they should be hooked to it. So, that customer life time value can be high.
The Hook framework proposed in the book has four steps to it. The concepts are built on the foundation of psychology and as Nir says – ‘behavioral design’.
Evolution has ensured the systematic and instant response of Human brain. So, automatically closing the eyelids is one example. Some amazing and very interesting theories and real research to explain behavior is covered in these wonderful books:
Behavior – Who Shapes our Choices and Decisions? Power of Social Influence
Superhuman, AI, Consciousness, Algorithms – Homo Deus: A Brief History of Tomorrow
Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind
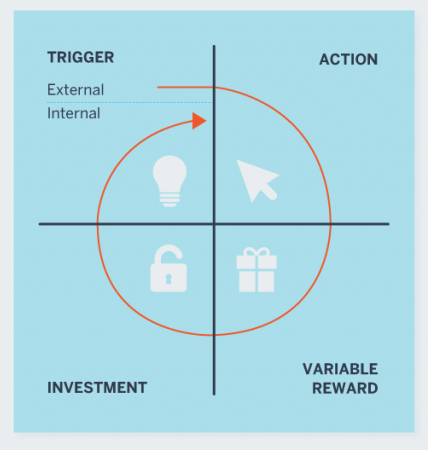
Four steps (TAVI) of the Hook model to create habit forming products.
Trigger
Triggers can be of two types – internal and external. Internal triggers are implicit and at emotional level. External triggers are explicit and have call to action embedded into it, for example, paid (advertisements) or earned (free) triggers.
Action
Action phase builds on the Fogg Behavior Model -> B = MAT, where B = behavior, M = motivation, A = ability, T = trigger. If any component is missing, it won’t work. For example, getting a cold call from telecaller executive would not lead to motivation to make a purchase. Second, important thing is the ability to take action. Many times, users are confused about what to do as a next step, for example, the login button on the website homepage. Here, the classical concepts of framing, anchoring, and scarcity effects are also discussed.
Variable Reward
Humans get bored very easily. You can notice that an infant rarely sticks to one toy! We need variable experiences and rewards (maybe that explains infidelity!). If you know that following steps will lead to same reward – you will get bored soon. So, firms should focus on variety of experiences to motivate consumers for repeat purchases.
Investment
The idea of investment builds on the concept of escalation of commitment. This is like sunk cost/opportunity cost phenomenon. Humans always exaggerates and value their efforts more. So, if government has spent some money in a project, they keep putting more money into it even they know its not going to work.
So, how this hook framework works? Here is an example to explain the four dimensions.
Example of creating habit forming products.
Social media such as Facebook, twitter or Instagram have built emotional trigger – the undying urge to check what is happening. That’s why we regular check our smartphones. The gratification and ease of use leads to action. The phone can be used anywhere anytime – imagine if social media can only be used on desktop, would it be as popular as it is now?
The variable rewards are the posts, comments, replies (appreciation?) from peers – the new joke, or a cat video!
Finally, the investment is that users have invested time and effort in building the social media profile and network. TO move from one network to another requires efforts and hence makes switching difficult.
The official site of the book.
You can buy the book at amazon (link below).
If you want to further explore the behaviorl side of decision making, check Misbehaving by Richard H. Thaler, a Nobel Laurette.