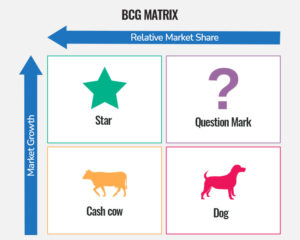
BCG Matrix (Boston Consulting Group Matrix), popularly known as Growth-Share Matrix, is a strategic tool used to analyze a company’s portfolio of products or business units. It categorizes these products or units into four quadrants based on their market growth rate and market share. The four quadrants in the BCG Matrix are:
Stars:
Products or business units with high market share in high-growth markets. Stars typically require significant investment to maintain their growth and market leadership. Indian example: Reliance Jio’s 4G services when they were introduced in India. At the time, Jio had a high market share in the rapidly growing 4G market, and they invested heavily in infrastructure and marketing to maintain their position.
Cash Cows:
Products or business units with a high market share in low-growth or mature markets. Cash cows generate a lot of revenue with minimal additional investment. Indian example: Hindustan Unilever’s (HUL) soap and detergent brands. These are well-established products with a high market share in a stable market, and they consistently generate profits for HUL.
Question Marks (or Problem Children):
Products or business units with low market share in high-growth markets. These are often in the early stages of development and require substantial investment to grow. Indian example: Electric vehicles (EVs) in India. The market for EVs is growing rapidly, but many companies are still trying to establish themselves and gain market share, which requires significant investment.
Dogs:
Products or business units with low market share in low-growth markets. Dogs do not offer much growth potential, and companies may consider divesting or discontinuing them if they cannot improve their market position. Indian example: Some traditional landline telephone services. With the rise of mobile phones and the decline of landline usage, these services have become low-growth and low-market-share products.
The Boston Consulting Group Matrix (BCG Matrix) helps companies make decisions about resource allocation and strategic focus. For example, companies may invest heavily in stars to turn them into cash cows, gradually divest from dogs, and carefully evaluate the potential of question marks.
It’s important to note that the BCG Matrix is a simplification of a company’s complex portfolio, and it has its limitations. Market growth rate and market share are not the only factors to consider in strategic decision-making, but the matrix can provide a useful starting point for analyzing a company’s products or business units.
The matrix is presented as 2X2 matrix. The X-axis is relative market share and Y-axis shows market growth.
Think and answer – where will you put the following on Boston Consulting Group Matrix?
Food delivery apps like Zomato, Swiggy, DineOut; e-commerce apps like amazon, myntra, flipkart, Coca Cola, ThumsUp, Maruti Baleno?